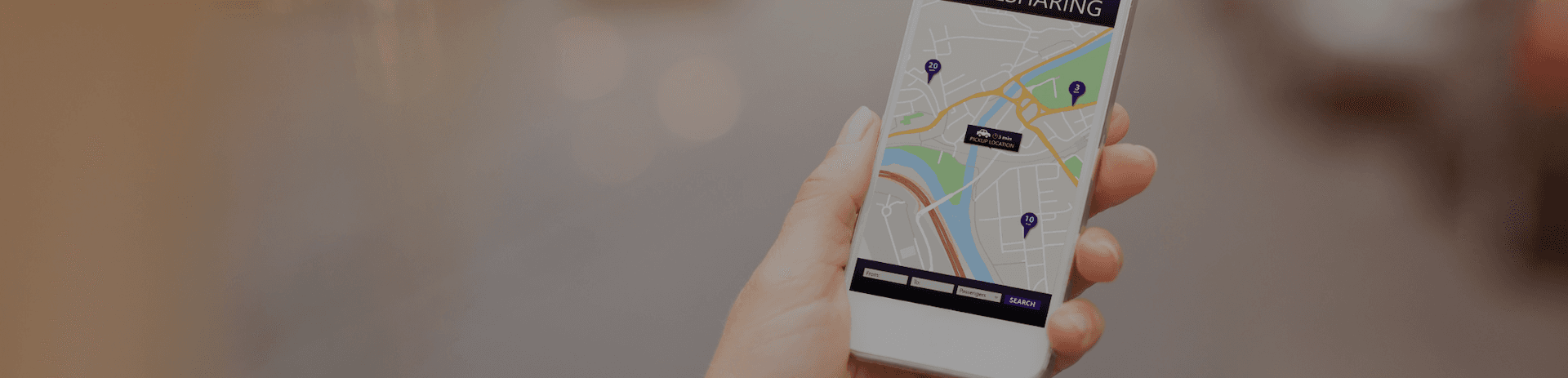
Image showing an example of an electronic public transport platform in Germany. Source: https://www.altexsoft.com/blog/engineering/public-transportation-apps-apis-and-platforms-maps-scheduling-trip-planning-and-mobile-ticketing/
Digitise Paratransit to Operate Through Electronic Transport Platforms
General Overview
Type of stakeholder
EICS Framework
Region of Reference
Africa
Asia
Australia
Europe
North-America
South-America
World
Description
This intervention refers to the digitisation of paratransit to operate through electronic transport platforms. Paratransit refers to transport services that supplement the larger public transport system, and transport services that generally don’t have fixed routes or timetables (e.g., minibus taxis in South Africa). The digitisation of these services will enable users to know when and where services will operate to and from, as well as to know information about their driver.
This aims to improve the safety and security of passengers, as they will no longer have to wait large amounts of time for the service to arrive if they know what the schedule is, and will be able to ensure that they only use safe routes.
Facts/Illustrations/Case studies
Types of Impact
Area Impacted
- To/from the stop/station/rank✓
- Waiting for train/bus/paratransit✓
- In the vehicle✓
- At interchanges✓
Time of Day of Impact
- Day-time travel✓
- Night-time travel✓
- Peak-time travel✓
- Off peak-time travel✓
Mode Impacted
- Bus✕
- Train✕
- Rideshare✓
- 4 wheelers informal✓
- 3 wheelers informal✓
- 2 wheelers informal✓
- Cycling✕
- Walking✕
Demographic impacted
- Girls✓
- Boys✓
- Adult Women✓
- Men✓
- Elderly Women✓
- LGBTQI+✓
Resources
SWOT Analysis
Allows passengers to plan their trips in a way that ensures their safety.
Scalable to suit budget and need
As soon as implementation stops, the benefits stop
Not effective in parts of the transport system where the intervention is not present
Information might be unreliable due to the ad hoc nature of paratransit and non-conformance by operators
To improve the passenger's overall safety when travelling using paratransit.
Improving the level of service offered by paratransit
Informal paratransit operators might be reluctant to digitise their information.
Data on informal paratransit may be hard to find in some countries.
Paratransit could lose some of its flexibility which is a key attribute of the mode
Effectiveness
Passengers, especially females, feel safer when they don’t have to wait long times for public transport to arrive, and can plan when and where they need to go to wait for the service. Additionally, passengers appreciate the extra information given to them through this platform, which is a benefit. As there is little literature to support this, confidence in these ratings is weak.
- Perception by (female) passengers
- Perception by governing bodies
- Level of confidence in these ratings
Implementation
This intervention takes a while to implement, as the electronic platform needs to be developed and the data collected. Benefits begin to ensue once the platform has been finished and passengers become aware of it. The data needs to be updated frequently to ensure accuracy and usefulness.
Implementation timeframe
- 0-1 year✓
- 1-3 years✓
- >3 years✕
Timeframe to realise benefits
- 0-1 year✕
- 1-3 years✓
- >3 years✓
Scale of Implementation
This intervention can be implemented at a local or city level.
Suburb
Ease of Implementation
This intervention is relatively easy to implement.
List of References

Europe

North America
2. Kearl, H. 2018. A National Study on Sexual Harassment and Assault. Virginia, United States.